Neurology
Neurology is a branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the nervous system. Neurology deals with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the central and peripheral nervous systems (and their subdivisions, the autonomic and somatic nervous systems), including their coverings, blood vessels, and all effector tissue, such as muscle. Neurological practice relies heavily on the field of neuroscience, which is the scientific study of the nervous system.
A neurologist is a physician specializing in neurology and trained to investigate, or diagnose and treat neurological disorders. Neurologists may also be involved in clinical research, clinical trials, and basic or translational research. While neurology is a nonsurgical specialty, its corresponding surgical specialty is neurosurgery.
What does a neurologist do?
Neurologists manage and treat neurological conditions, or problems with the nervous system. Symptoms that commonly require a neurologist include:
- coordination problems
- muscle weakness
- a change in sensation
- confusion
- dizziness
People who are having problems with their senses, such as touch, vision, or smell, may also need to see a neurologist. Problems with senses are sometimes caused by nervous system disorders.
Neurologist subspecialties
Because the nervous system is complex, a neurologist may specialize in a specific area. They will do a fellowship in that area after residency training. Subspecialties have evolved to narrow a doctor’s focus.
There are many subspecialties. Some examples of subspecialties include:
- headache medicine
- neuromuscular medicine
- neuromuscular medicine
- neuro-oncology
- geriatric neurology
- autonomic disorders
- vascular (stroke care)
- child neurology
- intervention neuroradiology
- epilepsy
Typical neurological procedures
During your first appointment with a neurologist, they will likely perform a physical exam and a neurological exam. A neurological exam will test muscle strength, reflexes, and coordination. Since different disorders can have similar symptoms, your neurologist may need more testing to make a diagnosis.
Neurologists may recommend a variety of procedures to help diagnose or treat a condition. These procedures may include:-
Lumbar puncture
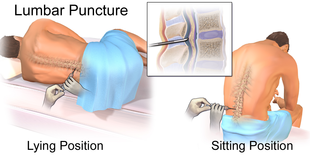
Your neurologist may use a lumbar puncture to test your spinal fluid. They may recommend the procedure if they believe your symptoms are caused by a problem in your nervous system that can be detected in your spinal fluid. The procedure involves inserting a needle into the spine after numbing it and taking a sample of spinal fluid.
-
Tensilon test
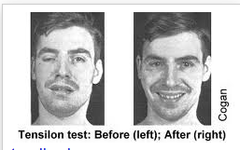
This procedure can help your neurologist diagnose myasthenia gravis. In this test, your doctor injects you with a medicine called Tensilon. Then they observe how it affects your muscle movements.
-
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
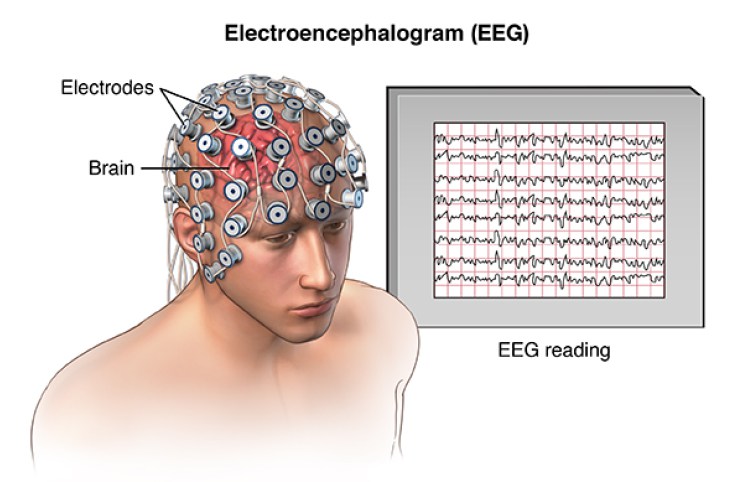
With electrodes applied to your scalp, an EEG measures electrical activity in the brain.
To make a diagnosis, a neurologist may use imaging tests such as:
Neurologists may use other types of tests, as well. Although they may not perform the test, they may order it, review it, and interpret the results.- computed tomography, or CT scan
- magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI scan
- positron emission tomography, or PET scan
Other diagnostic procedures include sleep studies and angiography. Angiography determines blockages in the blood vessels going to the brain.
